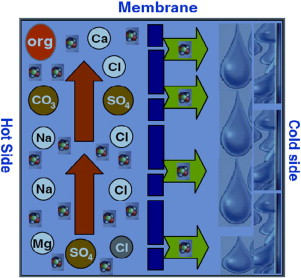
Membrane distillation (MD) is a hybrid thermal-membrane desalination process that uses low-grade waste heat and a hydrophobic membrane to produce high quality distillate. The MD process can treat highly saline brines that conventional desalination processes cannot treat.
These unique features of the MD process make it an ideal candidate to desalinate concentrated brines from thermal desalination plants, to augment fresh water production from existing facilities.
A consortium consisting of the ConocoPhillips Global Water Sustainability Center, Qatar University, and Qatar Electricity & Water Company has been formed to evaluate the application of MD for the desalination of concentrated brines from thermal plants.
Five different MD technologies were evaluated initially, and the two most suitable technologies were selected for field-testing. The pilot units A and B are based on multi-effect vacuum and air gap MD technologies, respectively.
These units were tested side-by-side to treat seawater and thermal brines at a full-scale thermal desalination plant in Qatar:
- Pilot unit A (multi-effect vacuum MD) showed a stable flux of 6.2 LMH under optimised conditions, with excellent salt rejection (>99.9%).
- Pilot unit B (air gap MD) achieved a distillate flux of 2.5 LMH, and salt rejection >98.9%.
Overall, membrane distillation is shown to be a feasible technology to produce potable quality water from the brines discharged from thermal desalination plants. Pretreatment is critical to avoid wetting and ensure proper system performance.


